The web has gone interplanetary.
Not really, but the web is evolving rapidly towards decentralization. To some, decentralization has become a motto or a phrase of rebellion against tech companies. The reality is, that decentralization is an alternative network architecture with pros and cons.
Using IPFS for static site or single page applications hosting has some neat benefits.
What are the differences between HTTP and IPFS?
HTTP can be thought of as a way for computers to directly communicate with one another. When an HTTP request is made, the device is sending some data to a specific location.
When you open an empty tab in your browser and navigate to the url https://google.com your network request connects with a DNS to lookup the IP address associated with the domain you are requesting.
If the domain is registered, the request is routed accordingly and the server at google.com sends a response (HTML) back to your computer.
IPFS can be thought of as a giant file system, where each file or directory has a unique identifier called a hash. So when you make a request via IPFS you are looking for a specific file or directory, but you don't care where it comes from.
What are the benefits of hosting a static site using IPFS?
💰 Cost
When data is requested from IPFS, you are searching for anyone on the network that has the file you are looking for. Then you store the file locally on the node you are running on your machine. As a result, that file is now accessible from two locations, the node you downloaded the file from and your own node.
So the next time you request the same file, you will retrieve it from your own storage as opposed to downloading it from some where else. The more visitors your site attracts, the more available it becomes on the peer-to-peer network, like an organic peer-to-peer CDN. With less traffic coming to your server, your server costs are reduced.
⛔️ Censorship
Files on IPFS are organically replicated. If someone tries to block traffic to your site or forces you to turn your server off, the file is still out there indefinitely on the system. Some call IPFS the permanent web because deleting every copy of the file from every node is near to impossible.
Extra References
HTTP is an open source protocol for computers to communicate over a network.
IPFS is an open source protocol for storing and sharing data on a peer-to-peer network.
DNS a system which maps human friendly names to IP addresses.
CDN a group of servers spread out in different locations.
Walkthrough Guide
Recommended Tools
- Create React App / Vite / NextJS (or any node/webpack based front end framework).
- Brave Browser. It has built in IPFS and Web3 Wallet support.
Steps
- Create a new repo or clone this one.
- Setup a Fleek Account at Fleek.co
- Select "Hosting" from the side bar and click "Add New Site"
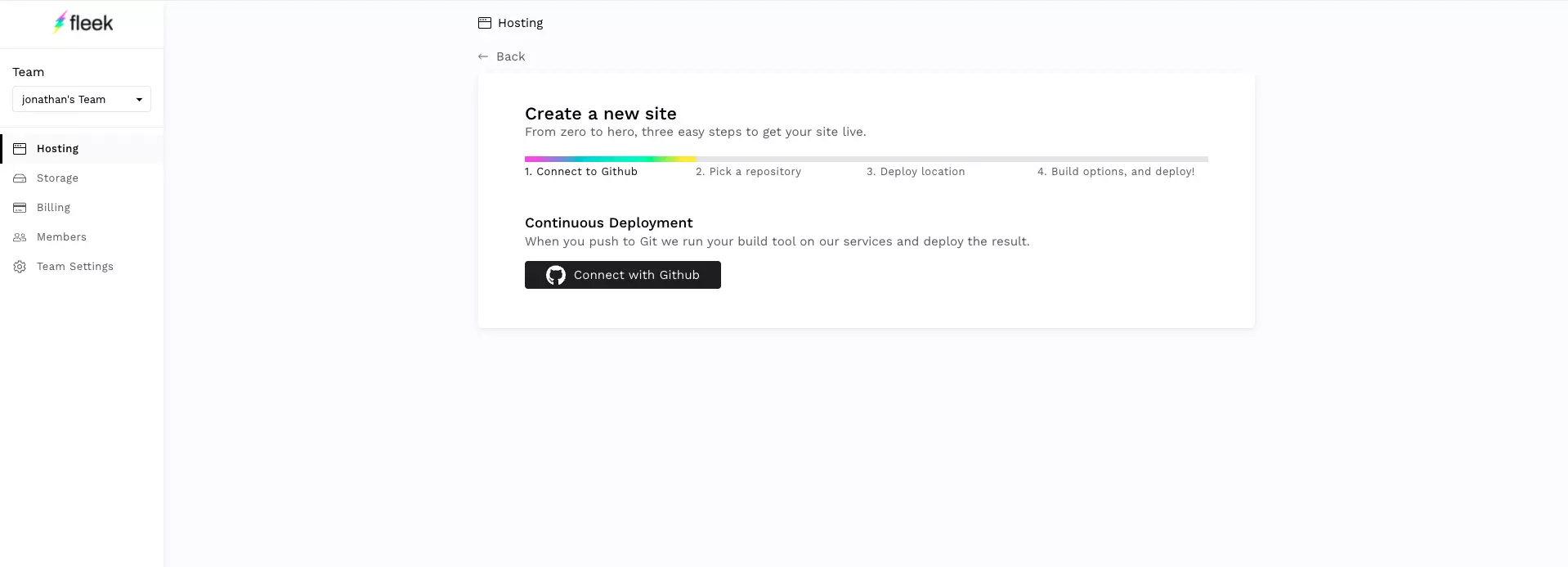
- Connect with Github.
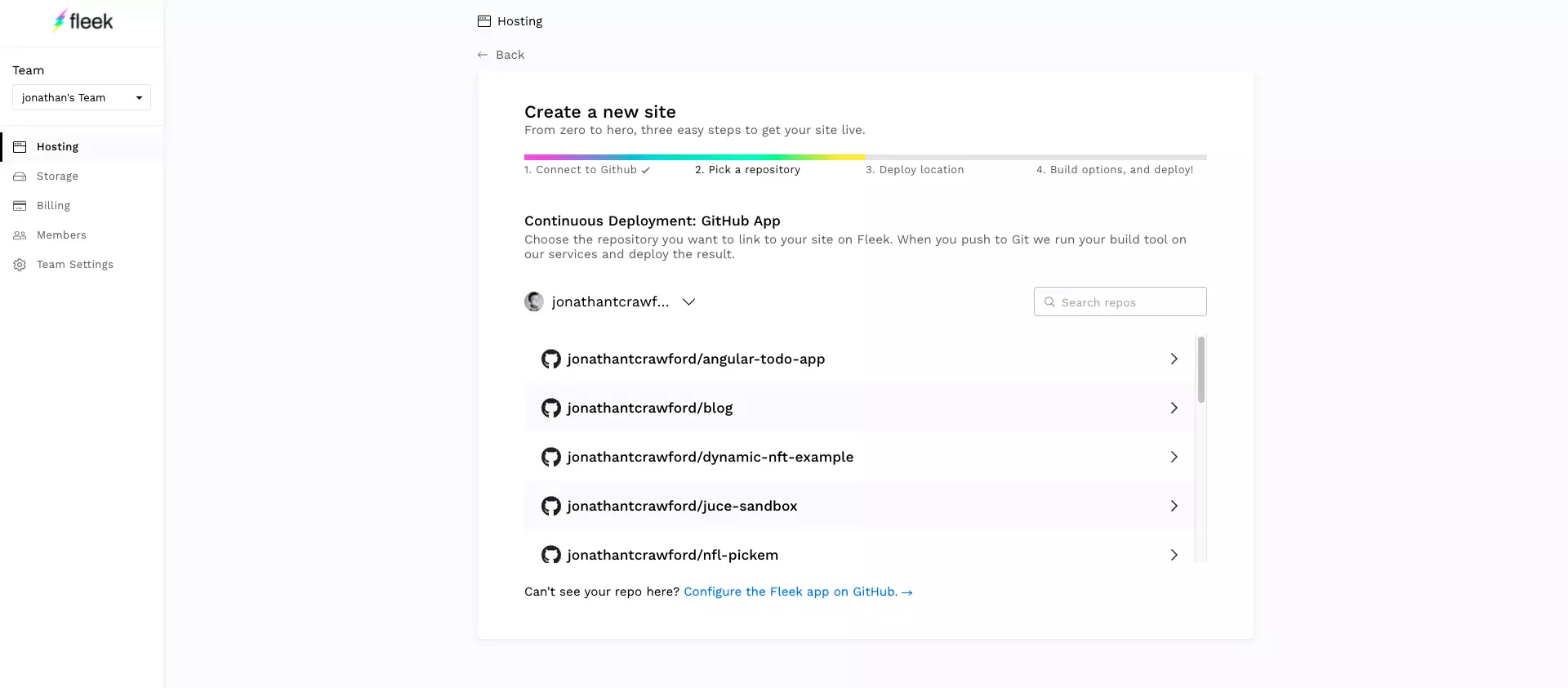
- Select a repo.
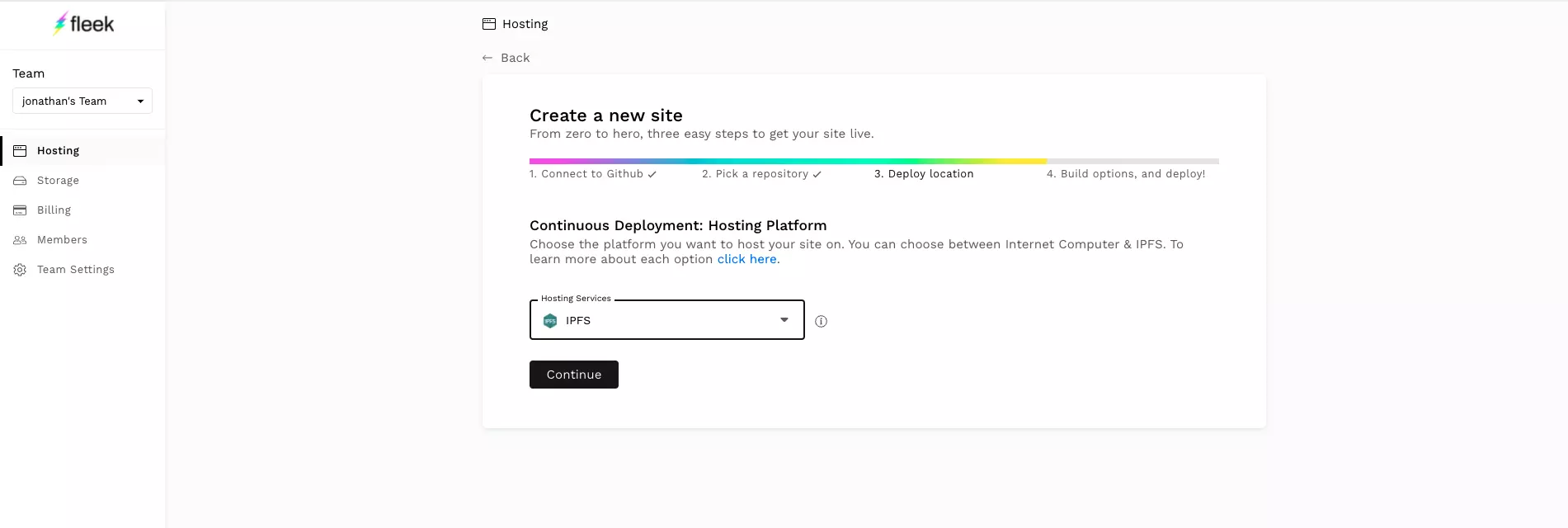
- Select "IPFS" from the Hosting Service dropdown.
- Choose the branch you want to deploy when commits are pushed.
If you are using one of the frameworks listed, feel free to select it. Otherwise, select "Other" for now. Then click "Deploy Site".
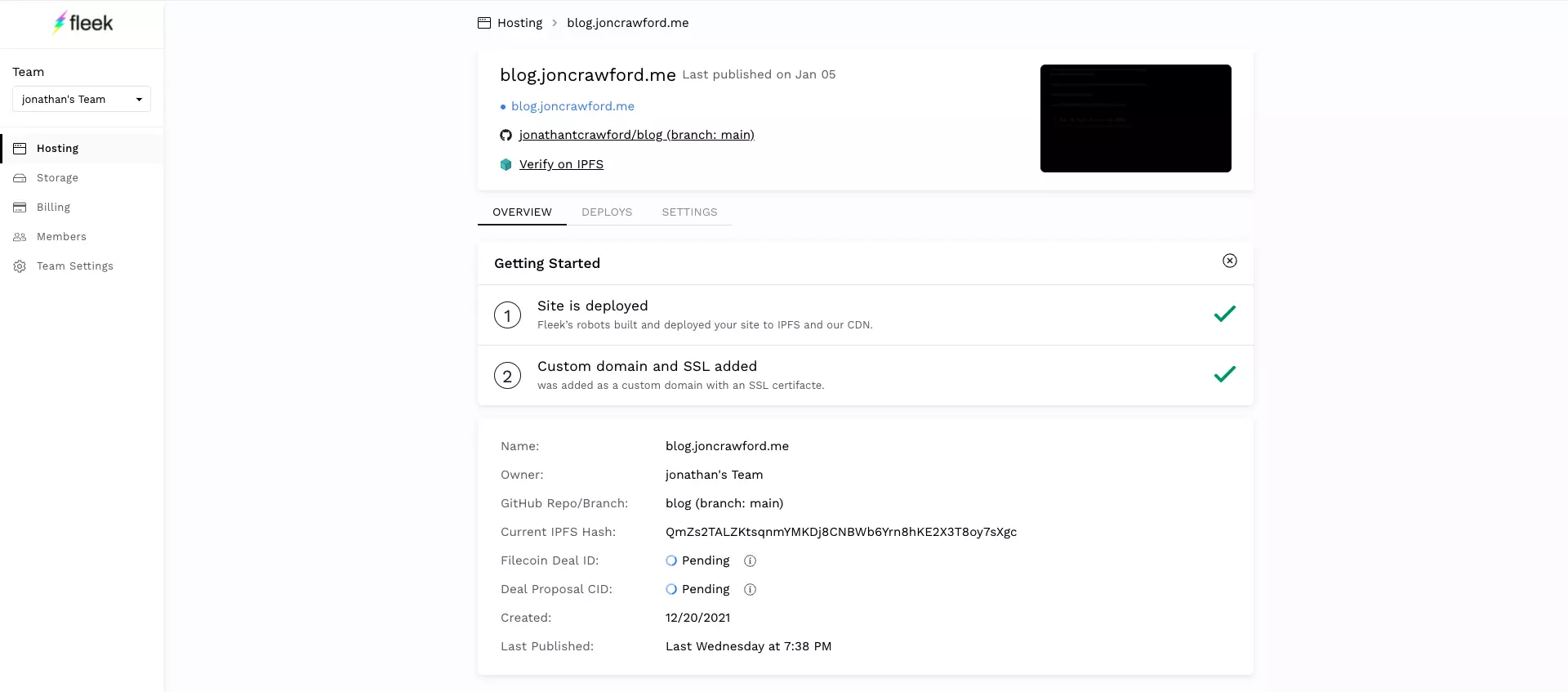
- You now have a configured Fleek Project! You can now view an overview of your project as well as a list of deployments and other settings.
- If you selected "Other" as your framework, during the project setup, your build most likely failed. It's because we still need to setup the build actions for the repo.
To fix this all we have to do is add a new file
.fleek.jsonto the root of the repo..fleek.json{ "build": { "image": "node:16", "command": "yarn && yarn build && echo $SOME_ENV", "publicDir": "dist", "baseDir": ".", "environment": { "SOME_ENV": "Build finished!" } } }.fleek.jsonfile. - Once you have added your
.fleek.jsonand pushed your changes. A new deployment should be triggered. - Fleek automatically creates a url for your site using the following format
{projectName}.on.fleek.co. - You can now setup an existing domain name if you own one.
ENS and HNS Domains
Fleek supports ENS and HNS Domains and they are fairly simple to setup. However, purchasing an ENS or HNS domain is a little more time consuming and tedious. The easiest way to obtain an HNS domain is through Namebase. (You will have to signup and add funds to your account in order to bid on available domains.) Once you place a bid and win an auction you can now point your domain to your IPFS hosted site!
Fleek makes this really easy. Just go to the "Domain Management" section of your Fleek project and scroll to the "HNS" section.
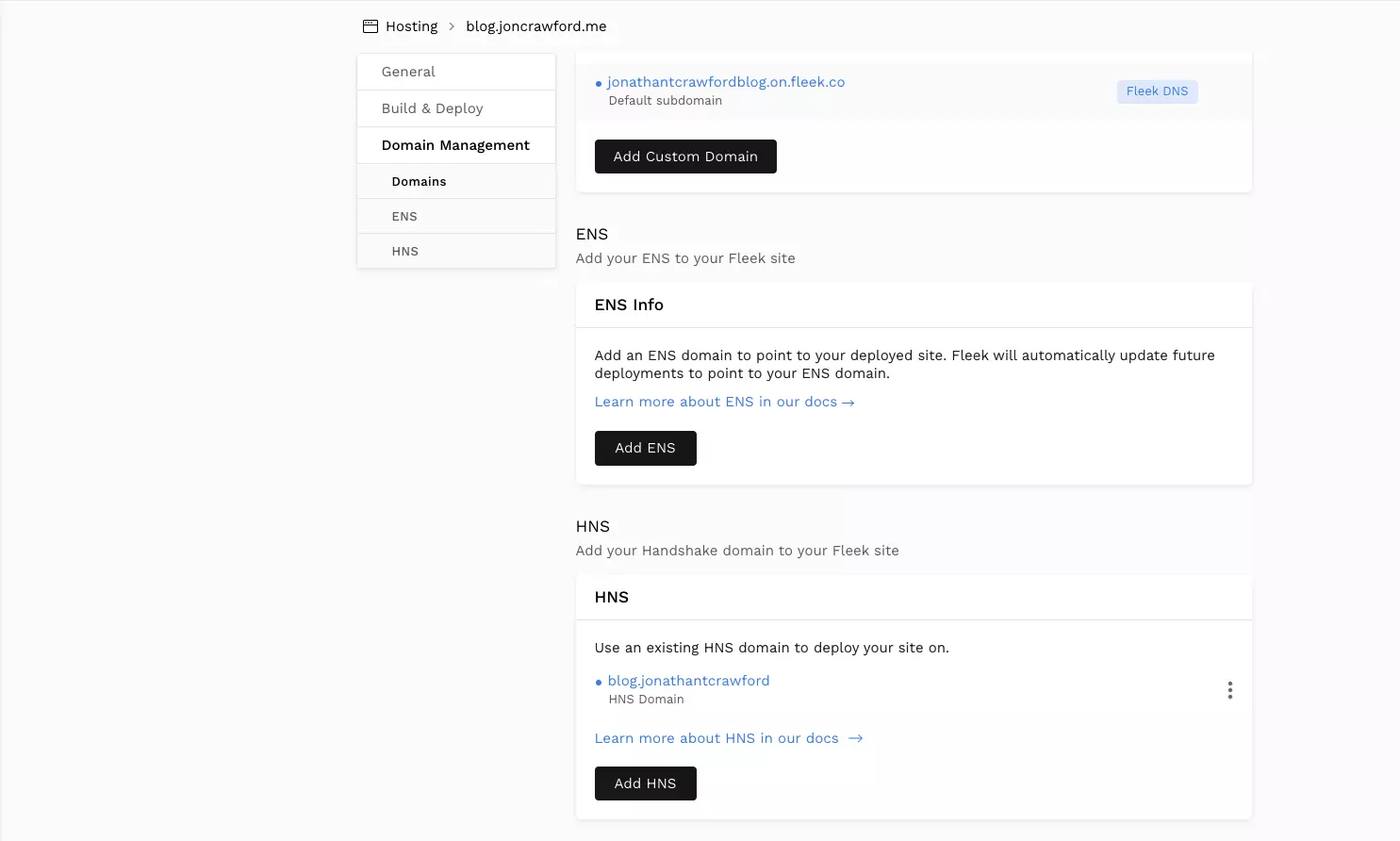
Click "Add HNS" and then follow the instructions. Fleek Domain Management Support
HNS Domain Limitations
HNS domains are not resolved by typical DNS servers. There are a few ways to resolve HNS domains, the easiest way is to edit your default DNS server on your computers network settings. The Handshake community maintains a DNS server that acts as a traditional DNS with the added support for resolving HNS domains. HDNS Setup
One final note, HNS domains do not support SSL and are therefore not PCI compliant. So, deploying a production application to an HNS domain is not very practical. However, the HNS team has made a lot of progress and I'm looking forward to what they do next.
Summary
IPFS is a practical decentralized file system that can coexist with centralized applications. Although, it is not fully integrated into the most popular browsers, I believe it will be soon enough. Until that day, do your own experimentation with IPFS. I hope this tutorial and repo helps you on your journey.